How we pay for stuff is relatively changing, “wave and pay” and “tap and go” is the new trend now! In a short period, users have become accustomed to waiving a card over a terminal to make purchases.
In the UK alone, 108 million contactless cards were issued in 2016,and contactless payments accounted for 34% of all card transactions. Looking at the rising adoption of contactless payments, this figure looks to rise significantly,not only in the UK but globally, as a growing number of retailers and consumer embrace the contactless cards.
Contactless payments work on NFC technology. The ease and intuitiveness of NFC technology have opened up many opportunities to innovate solutions and transform the banking ecosystem further. It hastrulybridged the gap between physical banking and the virtual world. Before looking at the nuances of how this technology has gotten a boot, lets first look at the regional statistics of contactless cards.
Region-wise Uptake of Contactless Payments
‘Contactless Payments’is the largestdriven markets now, dominated wholly by the mobile devices.
- In 2016, Europe dominated the market owing to the growing adoption of contactless smart cards. According to the statistics provided by com, £2,903.2 million was spent in the UK in November 2016 alone using contactless cards and 324.5 million contactless transactions made.
- Asia-Pacific region ranked second after Europeand is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period due to the relatively fast adoption of NFC-enabled contactless devices and wearable devices.
- The North American region will also display a sound growth backed by a large consumer base of mobile phone users.
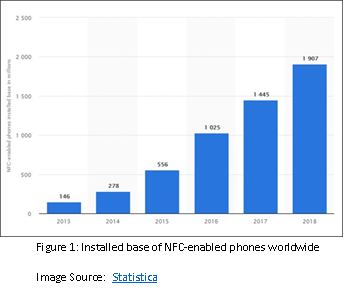
With the fast diffusion rate of smartphones, the percentage of people using mobile and NFC wallet services has been growing over time. Statistica research estimates that in 2018 approximately 1907 million installed bases of NFC-enabled phones will be available worldwide (Figure 1).
About the Mass Market Uptake of Contactless Payments!
You’re familiar with NFC technology if you’ve used the Google Wallet on your Android deviceor Apple Pay on your iPhone device. With a couple of quick steps on the mobile screen and a tap on a terminal near a cash register, the mobile deviceconfirms a payment from your virtual wallet to the retailer.
Eradicating the need to carry cash everywhere has led to comfortable and secure payment option. Consumers can make use of mobile wallet on their mobile devices to make transactions faster. With contactless payment, theconsumer is not required even to sign or enter his pin number.
Contactless payments have highly streamlined the process for the merchants and have reduced the cash handling, operating cost, and thus improved the efficiency. As the entire process has transformed the checkout experience for customers, it has increased customer spending, increased frequency of purchases, increased loyalty, thus increasing the revenue for merchants.
Contactless payments have also benefitted the issuer’sthrough:
- Competitive differentiation
- More consumer satisfaction
- Low-value transactions
- Branding opportunities with payment partners
Fraud losses on contactless cards have found to remain consistently low. The tap-and-go card fraud in Australia has reduced by 50% of conventional card fraud according to Visa.
The innovation in the contactless technology continues to grow as, mobile phones, wearables, mini cards, and stickers are all enabled with contactless payment. With the rise in the contactless payments on mobile phones in a big way, the technology will surelysee growth in the years to come.
Hurdles inFew Steps? But a Solution on the Way!!!
With all the momentum and innovation around NFC wallets, security is a huge concern to issuers, merchants, payment networks and users. Demonstrated by the number of data breaches that have plagued thebanking system, data security in payment is essential as consumer adoption grows.
Also, NFC based technology requires high infrastructure in terms of hardware, software and communication elements.This remains the costly affair for the banksin terms of both capital investment and recurring operational expenses.As a result, cost and standardization are the main concerns thatbanksneeds to address in the deployment and development of a standard contactless payment solution.
Unfortunately, NFC technologyis not a thorough security safeguard. It needs another layer of security toachieve the required level of confidence.
“Enter HCE and Tokenisation!”
All of thishaspavedthe way forTokenization and HCE (Host Card Emulation) ad to emerge as a new defense against payment frauds.
How does tokenization help? By aiming to lower the value of sensitive data stored on mobile devices and transmitted during payment. It does do by replacing the 16-digit card number with virtually substituted credentials that limit the impact of a card theft or a data breach.
Since tokens don’t carry the user’s primary account number, it is safer than magnetic strips, and even if it is hacked, there would not be anything of use asthe entire data is devalued.
On the other hand, in HCE, the card to be emulated is provisioned into the secure element on the device through an application.The secure element performs the communication with the NFC terminal, and nootherapplication is involved in the transaction at all.This in turn reduces complexities and the cost of thetransaction,asthe cloud server takes all the processing care.
As the transaction has to pass through the tech’s cloud servers for successful completion, HCE overcomes the safety concern in cases of a stolen mobile phone.
For banks, combining tokenization with techniques to encrypt sensitive data in the code of mobile payment applications is a good solution to secure HCE.
A Likely Future Roadmap
Banksneed to include a greater range of financial services by combining payments with related location-sensitive marketing and advertising for consumers. Widening the service offering means that banks must meet the evolving customer demands, adapt to local market conditions and cope with shifting regulatory environments.
At the same time, banks will have to engage in new ways with a widening set of ecosystem partners and stakeholders to ensure that the value chains are incentivised.
The future of contactless payments may allow people to make payments by waving their hands over a sensor. Still, this looks to be a more sci-fi based situation and will involve a lot of legal and ethical considerations.
A better and exciting area of development is the ‘Biometric way.’Although introduced at a smaller scale, this method will flourish in the future with simple facial, fingerprint, and finger vein recognition, allowing the customers to make payments by just taking a selfie.
As the trend for contactless payment develops in the coming years, TVs, tablets, and laptops will be NFC wallet equipped and act as payment terminals
Some Final Words…
Banks need to provide the customers with a seamless transaction experienceand given the potential positive effects of the adoption of contactless payments and NFC wallets, it is crucial to address the barriers where possible.
One solution can be standardization to reduce the technical barriers faced by the banks. Apart from this initiative, a technological and service-based development needs to be adopted by banks to enable efficient use of NFC wallets.
So, to use an NFCwallet services for enabling hassle-free contactless payments, banks need to embark on a solution that is compatible with their internal environment and as well as the infrastructure.
 Techosta Where Tech Starts From
Techosta Where Tech Starts From